El role de la IA en la iluminación.
La industria de la iluminación emplea habitualmente técnicas novedosas en el diseño y el control del alumbrado. Entre los cambios transformadores más significativos del sector se encuentran la evolución de la bombilla y la introducción de componentes de iluminación interconectados que aplican protocolos como DALI.
En el contexto de los sistemas de control de iluminación, el ámbito de aplicación de la IA es muy amplio, y afecta a las distintas etapas del ciclo de vida de la iluminación, como el diseño, la instalación, la puesta en marcha y la configuración.
Por ejemplo, una red de componentes de iluminación con capacidad de autoaprendizaje puede comunicarse y configurarse por sí misma sin necesidad de intervención humana, de forma similar a los sistemas de puesta en marcha automática que se utilizan en el sector informático. Esta red reducirá el tiempo necesario para poner en marcha nuevas instalaciones de iluminación.
Al observar y medir el ambiente interior, un sistema de iluminación basado en la IA puede optimizar y ajustar los parámetros de iluminación en consecuencia para influir en la experiencia y en el bienestar del usuario.

El role de la IA en la iluminación.
La industria de la iluminación emplea habitualmente técnicas novedosas en el diseño y el control del alumbrado. Entre los cambios transformadores más significativos del sector se encuentran la evolución de la bombilla y la introducción de componentes de iluminación interconectados que aplican protocolos como DALI.
En el contexto de los sistemas de control de iluminación, el ámbito de aplicación de la IA es muy amplio, y afecta a las distintas etapas del ciclo de vida de la iluminación, como el diseño, la instalación, la puesta en marcha y la configuración.
Por ejemplo, una red de componentes de iluminación con capacidad de autoaprendizaje puede comunicarse y configurarse por sí misma sin necesidad de intervención humana, de forma similar a los sistemas de puesta en marcha automática que se utilizan en el sector informático. Esta red reducirá el tiempo necesario para poner en marcha nuevas instalaciones de iluminación.
Al observar y medir el ambiente interior, un sistema de iluminación basado en la IA puede optimizar y ajustar los parámetros de iluminación en consecuencia para influir en la experiencia y en el bienestar del usuario.
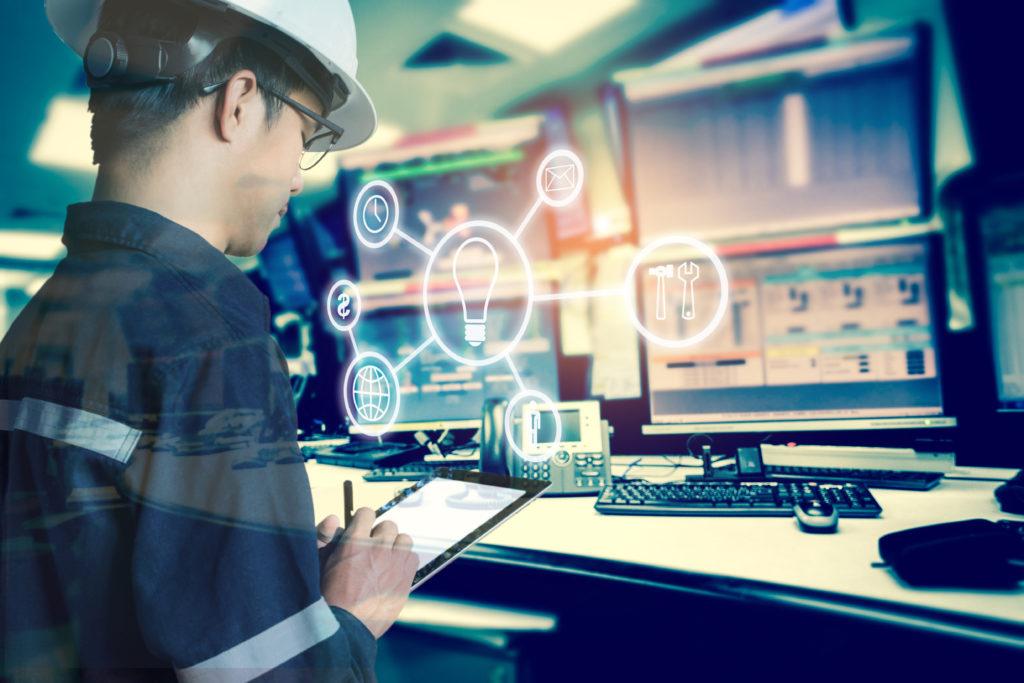


La iluminación con IA puede beneficiar a muchas personas.
La utilidad de un sistema de este tipo no se limita a los usuarios finales o a los inquilinos, sino que se extiende a otras partes interesadas, como los propietarios de edificios y los gestores de instalaciones.
Una red de componentes de iluminación basada en datos genera continuamente datos que se recogen y almacenan en un servidor centralizado. Los algoritmos de IA pueden ejecutarse en el componente fuente, como un sensor, para tomar decisiones descentralizadas en tiempo real, o en un servidor para tomar decisiones centralizadas.
Además, los datos recogidos se aplican a otros sistemas de gestión de edificios (BMS), como los de calefacción, ventilación y aire acondicionado (HVAC), o la gestión de accesos.
La iluminación con IA puede beneficiar a muchas personas.
La utilidad de un sistema de este tipo no se limita a los usuarios finales o a los inquilinos, sino que se extiende a otras partes interesadas, como los propietarios de edificios y los gestores de instalaciones.
Una red de componentes de iluminación basada en datos genera continuamente datos que se recogen y almacenan en un servidor centralizado. Los algoritmos de IA pueden ejecutarse en el componente fuente, como un sensor, para tomar decisiones descentralizadas en tiempo real, o en un servidor para tomar decisiones centralizadas.
Además, los datos recogidos se aplican a otros sistemas de gestión de edificios (BMS), como los de calefacción, ventilación y aire acondicionado (HVAC), o la gestión de accesos.

Iluminación y privacidad de la IA.
A pesar de todas sus ventajas, en general, la tecnología de IA no está exenta de defectos.
Las cámaras dotadas de IA pueden detectar con precisión la ocupación y los movimientos en una habitación o espacio, pero la información visual requeriría un estricto cumplimiento de las leyes de privacidad. Otro reto importante es la limitada comprensión humana de la IA, que también impide su rápida adopción.
Por suerte, como la iluminación artificialmente inteligente suele funcionar con sensores de detección de movimiento PIR, hay muy pocas preocupaciones en torno a la privacidad. Muchas empresas utilizan los sistemas de iluminación artificialmente inteligentes como una solución probada y fiable para mejorar la experiencia del usuario, la comodidad y la productividad, al tiempo que consiguen un ahorro tangible de energía y costes.

Iluminación y privacidad de la IA.
A pesar de todas sus ventajas, en general, la tecnología de IA no está exenta de defectos.
Las cámaras dotadas de IA pueden detectar con precisión la ocupación y los movimientos en una habitación o espacio, pero la información visual requeriría un estricto cumplimiento de las leyes de privacidad. Otro reto importante es la limitada comprensión humana de la IA, que también impide su rápida adopción.
Por suerte, como la iluminación artificialmente inteligente suele funcionar con sensores de detección de movimiento PIR, hay muy pocas preocupaciones en torno a la privacidad. Muchas empresas utilizan los sistemas de iluminación artificialmente inteligentes como una solución probada y fiable para mejorar la experiencia del usuario, la comodidad y la productividad, al tiempo que consiguen un ahorro tangible de energía y costes.

Helvar ActiveAhead:
Iluminación inalámbrica inteligente de forma sencilla.

HELVAR ACTIVEAHEAD® es una solución de iluminación inalámbrica realmente inteligente y escalable.
Sus exclusivas capacidades de aprendizaje automático ofrecen la eficiencia definitiva a nivel de configuración y operaciones.
¡Vea la inteligencia artificial en acción con ActiveAhead!
Estudio de caso de Ramboll
ActiveAhead, la solución de control de iluminación inalámbrica con aprendizaje automático y a prueba de futuro, fue la elegida en la sede central de Ramboll para cubrir las plantas de oficinas y el aparcamiento, con aproximadamente 3000 unidades de control ActiveAhead instaladas en total.

Estudio de caso de Wärtsilä
El Wärtsilä Campus está equipado con ActiveAhead, el primer sistema de control de iluminación del mundo basado en inteligencia artificial. Wärtsilä se decantó por esta solución inalámbrica, con aprendizaje automático y a prueba de futuro porque deseaban que todos los sistemas de sus edificios contaran con tecnología de última generación.